From the Founder’s Desk:
We have had an exciting start to the year! Lots of new launches in the Indian Electric Mobility landscape and a growing focus on clean mobility across stakeholders including in policy-making at the Central Government level.
As deal activity increases in Mobility and Sustainability, we are looking to partner at mid-to-senior levels. If you are or know of a creative, entrepreneurial investment banker with a passion for catalysing global climate investments in India, do write to me directly at vasudha@ostara.co.in
On with our newsletter for this month…
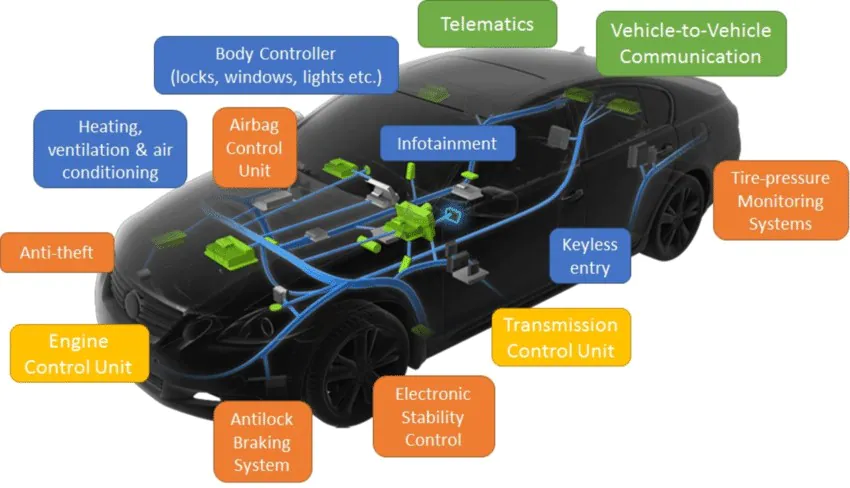
An Electric Vehicle (EV) consists of an interconnected system of electronics and connection networks that manage the various functions in the vehicle, including the BMS (which, for instance, measures the battery temperature and accordingly, initiates the cooling or heating operation by sending a signal to the ECU), among many others such as the electronics of the powertrain, the infotainment system, etc. all of which we call the Internal Network of the EV.
What does the EV’s Internal Network do?
The internal network helps:
- manage the distribution of power to different systems and components,
- control the motor, such as its torque and speed, as well as manage regenerative braking,
- manage the charging process, monitoring the battery’s SoC (state of charge) and temperature during charging, and
- collect data for vehicle diagnostics and performance analysis.
In our earlier editions, we’ve talked about the powertrain, the motor, and even the battery, which constitute the internal network’s hardware components. These components are connected through an Electronic and Electrical communications network, called the Controller Area Network (CAN Bus).
So what is the CAN Bus?
CAN is a robust and reliable communication protocol widely used in the automotive industry due to its high data transmission rate and low complexity. It was introduced in 1986 by Robert Bosch, at the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) congress.
Think of the EV as a human body. Just as the body has various parts in organs, muscles, and bones, so does the EV, in the many constituent components and functions (ECUs to be precise, we’ll talk about them in a bit), and the primary system assisting the coordination of all these parts, is the CAN bus, which functions as the central nervous system, enabling communication across the EV.
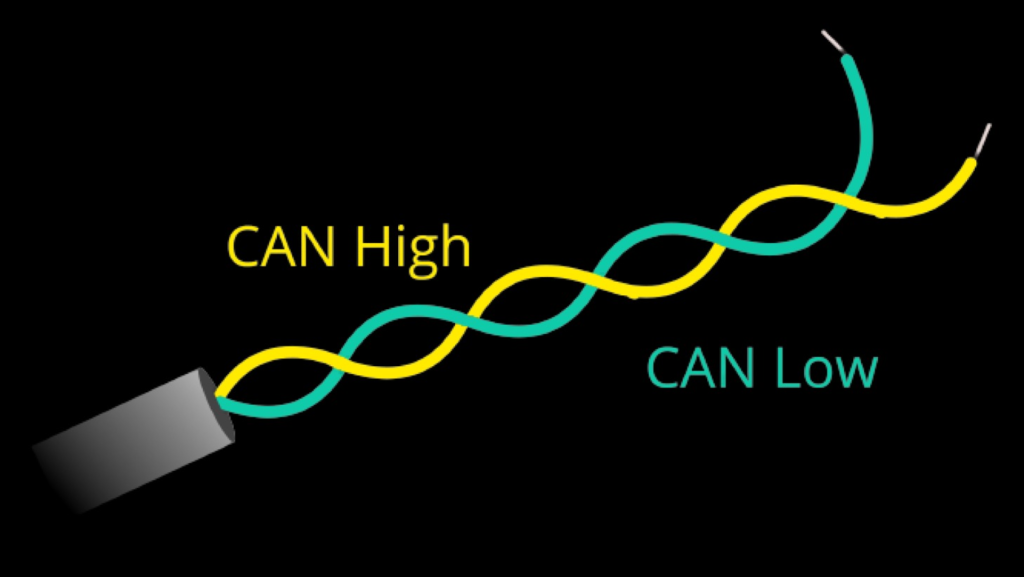
The CAN bus is a 2-wired communication bus, i.e., one wire is used for transmitting data (often referred to as the “CAN high” line) and the other wire is used for receiving data (often referred to as the “CAN low” line).
The CAN bus is used to connect various ECUs within the EV. Each ECU has a unique identifier (known as an “address”) and can use the CAN bus to send and receive messages with other ECUs in the vehicle.
Overall, the CAN bus plays a critical role in ensuring an electric vehicle’s safe and efficient operation, and its design and implementation must meet strict safety and reliability standards.
ECU
The internal network contains several regional systems responsible for the function of some sections of the EV. There is an ECU, which acts as a node for the CAN bus, receiving information, and relaying it across.
An electronic control unit (ECU) is a small device inside a vehicle that controls one or several electrical systems in that vehicle. It tells electrical systems what to do and how to operate. ECUs consist of one or more microcontroller CPUs (Central Processing Unit, integrated circuits designed to perform specific tasks) and embedded software.
While the entire powertrain of an EV is much simpler than that of their ICE counterparts, the number and sophistication of the electronic control units (ECUs) distributed around road-going EVs, in particular, continue to grow as more functions within the powertrain, chassis systems, driver aids and automation require computer control. Also, more of them have to be certified to safety standards, particularly ISO 26262, which governs electrical and electronic safety in road vehicles.
How the ECU works
An ECU receives input from one or several parts of the vehicle and uses that information to take action if needed. Let’s look at some examples:

Bringing it all together
In an automotive CAN bus system, ECUs can for e.g., be the engine control unit, airbags, audio system etc. A modern car may have up to 70 ECUs – and each of them may have information that needs to be shared with other parts of the network. This is where the CAN standard comes in handy. The CAN bus system enables each ECU to communicate with all other ECUs – without complex dedicated wiring, but a simple 2-wire system as shown above.
ECUs & AUTOSAR Architecture
AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture (AUTOSAR), founded in 2003, is a development partnership of automotive companies that seek to establish an open and standardised software architecture for automotive electronic control units (ECUs).
AUTOSAR is an open and standard software architecture which was jointly developed by automobile manufacturers, suppliers and tool developers. As of February 2023, there are 350+ companies in this partnership.
Following the AUTOSAR standard made it possible to have a common software stack, leading to scalability to different vehicle and platform variants, transferability of software and easier updation during the product life cycle.
Auto Expo Showcase: 13-18 January 2023
Auto Expo is the biggest automotive event in India that takes place every two years, organised by the Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM), which is the apex governing body of the Indian automobile manufacturing industry.
2023 saw the beloved event coming for its 16th edition, returning after three years, rather than the usual two. The event witnessed some exciting activity in the EV space:
4W Segment
From Maruti Suzuki, we saw the evX concept, which is set to become the OEMs first electric
vehicle. Tata showcased multiple vehicles, in the 4W as well CV segments. The 4W segments saw Tata Tiago Blitz EV, Tata Harrier EV, Tata Sierra EV, as well as their concept, Avinya.
Commercial Vehicle Segment
In the CV segments, we saw multiple OEMs showcase upcoming models of small-to-medium trucks as well as buses, including the Tata Group, Omega Seiki, JBM, Greaves Electric, etc. Ashok Leyland showcased its electric truck, the Boss EV, and Jupiter Wagons debuted their EV commercial vehicle line with the JEM Tez and the EV Star CC.
2W Segment
The 2W segment was bustling with activity, with several interesting displays. Ampere Vehicles showcased their Primus e-scooter while Liger Mobility presented their Liger X and X+ models. Matter Energy showcased its new concepts in the form of Concept EXE and Concept UT. Tork displayed their Kratos X e-Bike, while Ultraviolette showcased their F99 racing platform. Motovolt launched their multi-purpose e-scooter, while Hero Motocorp displayed their Vida V1 model.