Hey Everyone!!
We are back with our monthly edition to dive into India’s recent Battery Waste Management Rules as well as feature select global actors in this space & their recycling technologies.
The potential value creation for EV battery recycling, estimated at $95 billion per year by 2040, is massive and is attracting attention from automotive OEMs, battery OEMs, and investors. Source: McKinsey insights
Happy Reading!
India’s Waste Management Policy – who does what!
The Indian government notified the Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022 late last year to ensure efficient management of and clear accountability for waste batteries in the country. Key definitions in this Policy include:
Battery materials include metals such as nickel, cobalt, lead, lithium, and other materials such as plastics, paper, etc.
‘End of Life battery’ refers to batteries that have been used, completed their intended use, and are not meant for refurbishment.
‘Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) means the responsibility of any Producer of Battery for environmentally sound management of Waste Battery.
The Producer:
- They must ensure batteries in the market meet collection and recycling targets, registering and renewing before 60 days of expiry.
- Central Pollution Control Board(CPCB) must be informed of any changes in EPR registration and permanent cessation of the battery.
- An EPR plan must be provided to CPCB by 30th June for the Battery manufactured in the preceding financial year including its quantity & weight, dry weight of Battery materials.
- Annual returns regarding the Waste Battery collected and recycled or refurbished must be filed.
Recycler
- It requires them to register with the State Pollution Control Board via the online portal.
- Must ensure that hazardous waste is managed according to the Hazardous and Other Wastes Management and Transboundary Movement Rules and other waste is managed according to the Solid Waste Management Rules, Plastic Waste Management Rules, and E Waste Management Rules.
- Quarterly Returns should include waste battery quantities, recycling compliance, and hazardous waste generation.
- Batteries Recycled must not exceed installed capacity while meeting minimum weight targets.
- A Committee reviews recovery targets for battery materials every 4 years.
Central Pollution Control Board
- It registers the Producers and ensures compliance with these rules.
- It shares EPR plans and registration details with the State Pollution Control Board.
- Periodic inspections and audits are conducted to enforce rule compliance. In case of violations, registration suspension or cancellation may occur.
- It publishes EPR certificates, a list of non-compliant producers, EPR plans, and annual returns.
- It establishes a stakeholder dialogue mechanism and forms a Committee to implement the rules, submitting reports and recommendations every six months to the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change.
Portal
- An online system for the registration and filing of returns by producers, recyclers, and refurbishers of Waste batteries within six months of the commencement of these rules.
- It reflects the audit details of the Producers and entities involved in recycling.
Target of EPR
The EPR targets new producers of batteries in the market, encompassing collection and 100% recycling goals.
- The regulation mandates a minimum collection of 70% of batteries placed in the market in the previous financial year, with 100% of collected batteries to be refurbished or recycled within a seven or fourteen-year cycle.
- Additionally, up to 60% of the average yearly quantity of batteries placed in the market can be carried forward to the next compliance cycle.
Source: Battery Waste Management
Key Players in the EV Recycling Value Chain:
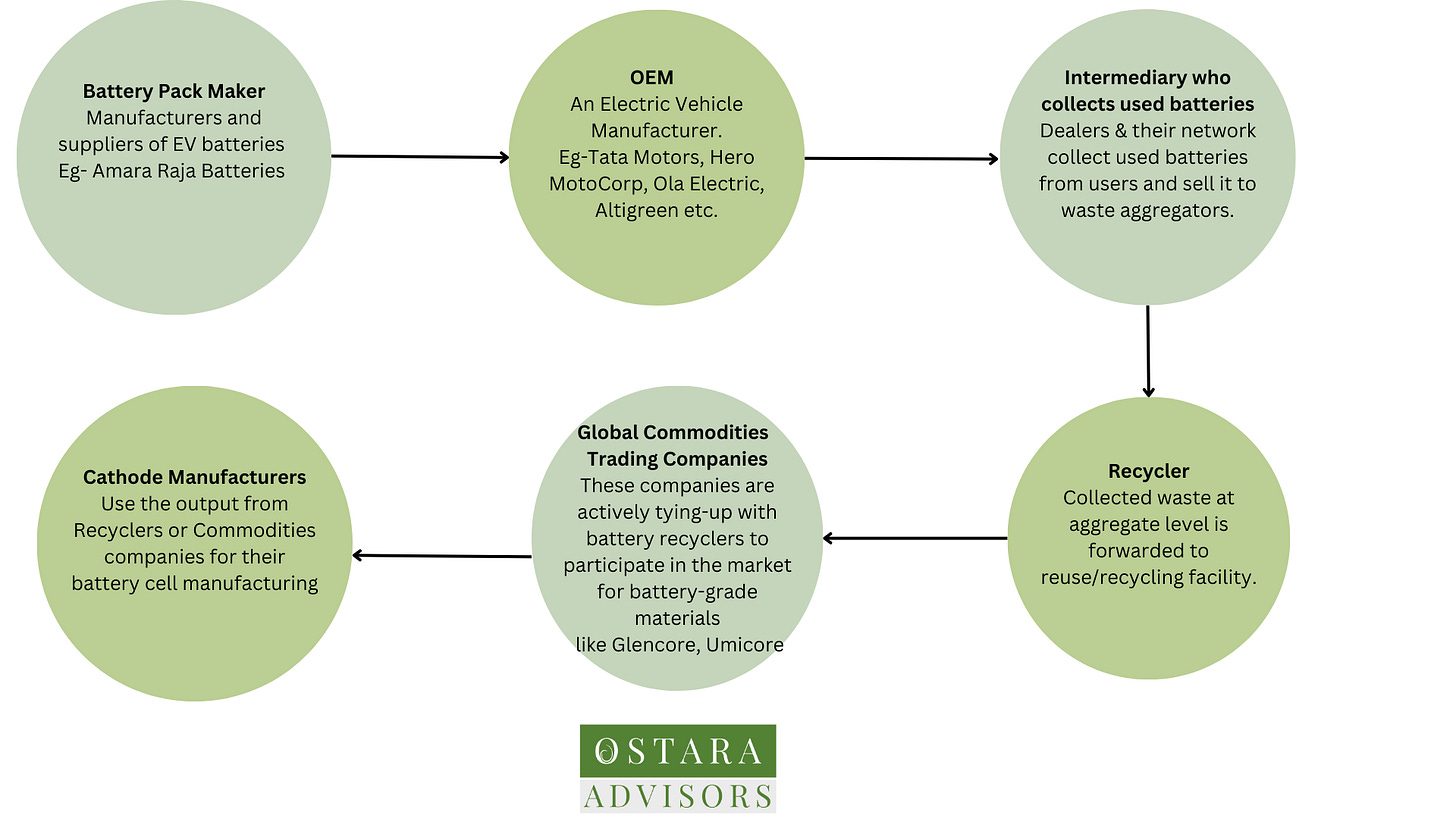
Source: Science News, Niti_Aayog
International Actors in this domain
Recycling companies — including American Battery Technology Company and Redwood Materials, both based in northern Nevada and headed by former Tesla engineers — say they are making the processes more efficient.
- American Battery Technology Company is a US-based battery recycling startup founded in 2011 by CEO Ryan Melsert. Their innovative approach utilizes machines to break down used batteries, replacing traditional hydrometallurgy.
They extract and sell lower-value components like plastic, aluminum, and steel, while their proprietary chemical reactions enable the extraction of valuable elements such as nickel, cobalt, manganese, and lithium.
This process achieves a recovery rate exceeding 90% for these high-value elements.
The Company is establishing partnerships with General Motors, Ford, and Stellantis (owners of multiple brands like Dodge, Jeep, and Maserati) to ensure that traded-in car batteries are sent for recycling.
- Redwood Materials, Inc., headquartered in Carson City, Nevada, was founded by JB Straubel, former Tesla CTO and co-founder. The company has partnered with Volkswagen, Toyota, Ford, and other automakers for battery collection and recycling initiatives.
Redwood’s advanced process can recover over 80% of lithium and 95-98% of nickel, copper, and cobalt from batteries, resulting in high-quality lithium carbonate for new battery production.
To support its expansion, Redwood Materials secured a $2 billion loan commitment from the Department of Energy. The funding will be utilized to construct and enhance a battery recycling facility near Reno, Nevada. The facility processes end-of-life electric vehicle batteries and automotive production scrap, generating raw materials used in the production of new EV battery cells.
In a significant economic development announcement, Redwood Materials revealed a $3.5 billion investment to establish operations in Berkeley County, South Carolina, creating 1,500 new jobs over the next decade.
- Li–Cycle is a Canadian clean technology company specializing in environmentally friendly lithium-ion battery recycling. Their process utilizes leaching instead of smelting, resulting in minimal waste, air emissions, and water consumption. The low-temperature process ensures a small environmental footprint.
Having raised a total of $1 billion in funding across 7 rounds, Li-Cycle recently secured a conditional $375 million loan from the Department of Energy. The funding will support the development of a battery material recycling facility near Rochester, New York. Read more
Some of the largest companies in the world are buying as much recycled battery metals as available, the challenge, right now, is really about who can scale up the quickest.
Source: CNBC
Do write in to us with topics in Climate-tech, Mobility, and New Energy that you’d like us to cover in future editions.
















