Hello Reader,
As the Sustainability wave sweeps the globe, it’s heartening to see the automotive industry taking a strong approach in this direction. This approach to production can redefine the way vehicles are designed, manufactured, used, and disposed of, by prioritizing the principles of Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, and Regenerate. By adopting circular economy principles, the automotive industry can reduce waste, conserve resources, and mitigate its environmental impact.
What is Circularity in the Automotive Industry?
Did you know that Circular economy approaches can help the automotive industry reduce the lifecycle carbon emissions per passenger km by up to 75% by 2030?
The term “circular economy” was first coined by Pierce and Turner in 1989 and refers to an alternative to the linear economy. It focuses on maintaining material value and eliminating waste, using the 3R principle: reduce, reuse, and recycle. This method minimizes resource usage, maximizing the reuse of old products. The circular economy is also known as a closed system of production, as it circulates used products as a basic resource. This sustainable approach to production is a healthier approach to the environment.
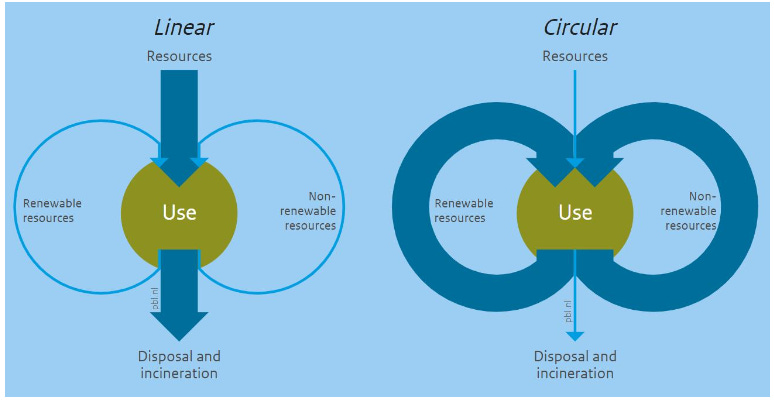
Source: Kenniskaarten, Impacx, Contec.
So what is a “Circular Car” and what are the key elements of this approach?
A circular car maximizes value to society, the environment, and the economy, and it efficiently utilizes resources and public goods. Accenture and WEF in their 2021 Report recommend 4 approaches to achieving Circular Economy in the automotive industry.
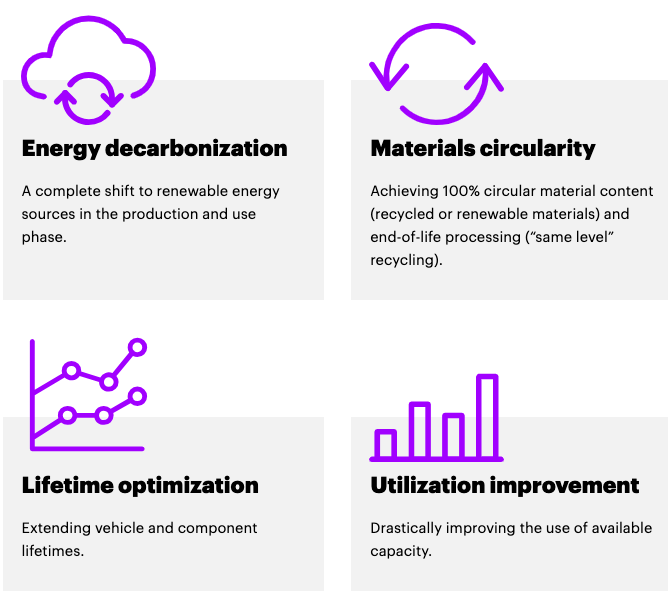
Source: Accenture – World Economic Forum Report 2021
The degree of circularity should be measured in terms of outcomes including lifecycle Co2 emissions or non-circular resource consumption per unit of passenger km.
Key Methods to implement these 4 approaches
- Remanufacturing is a significant aspect of the circular economy, with benefits such as the conservation of natural resources, reduced waste, a smaller carbon footprint, and lower costs. Automotive components are commonly remanufactured by companies like ZF, Robert Bosch, Carwood, IM Group, and Valeo, as well as automakers like Renault. The Refectory in Europe is Europe’s first circular economy factory focused on mobility, built around four pillars: Retrofit (vehicle life extension), Re-energy (green energy management), Re-cycle (resource management optimization), and Re-start (accessible innovation).
- Recycling is another important aspect of the circular economy, with recycling plastic, steel, aluminum, and tires offering environmental benefits. Closed-loop recycling is a major trend that reduces natural resource usage, pollution, and landfill burden used by Nissan Rogue. Automakers like General Motors, Honda, Nissan, Ford, Volkswagen, and Chrysler are involved in plastics recycling, with Honda making mud guards and splash guards from recycled scrap bumpers. Steel is almost 100% recyclable, and most car bodies contain approximately 25% recycled steel. Companies like Wastefront, Bridgestone, and Michelin are showcasing innovative approaches to tire recycling.
- Product life extension, where vehicle parts are proactively serviced before they develop any faults, thereby extending their useful life. The automotive industry is focusing on increasing the useful life of products, including tire and battery life extension, servicing electronic components, and deploying predictive maintenance systems. Retreading tires can extend a tire’s life by at least 200%, saving fleets $3 billion annually in tire-related costs. Predictive maintenance systems (PMS) are being used to detect component faults before they occur and predict repair needs. Continental Tyres India launched the Conti Bharosa warranty program in July 2021, offering a 5-year warranty on truck and bus tires. Electronic components are being serviced instead of discarded, reducing electronic waste in landfills. Companies like ReJoule provide rapid diagnostic testing for EV batteries entering second-life applications.
- Sustainable material use, where innovative, eco-friendly materials such as bio-plastics are incorporated into new cars. This includes alternatives like recycled polyester microfiber, vegan leather from grape skins and seeds, compressed wood composites, and natural fibers like Amplitex. The development of organized scrapyard markets, repurposing EOL batteries for second-life applications, and investments in eco-friendly sustainable materials are necessary, especially in India.Source: Suppliers Partnership, Mobility Outlook.
How can Technology solve for Circularity in the Automotive Industry?
Predictive Maintenance: Cloud-connected data infrastructure allows for monitoring vehicle performance and customer behavior by enabling the “Software-defined vehicle” (SDV) concept. This data, combined with machine learning and advanced analytics, can help keep vehicles and components in use longer, reduce emissions, and minimize waste at the end of a product’s life cycle.
Battery & Vehicle Re-use & Recycling: Automated dismantling systems are used to efficiently disassemble end-of-life vehicles and recover valuable components and materials for reuse. As Battery Recycling and Second-Life Applications become more common, technology can enable Residual Value assessment of EV batteries for stationary energy storage, providing a second life and maximizing resource utilization.
Shared Mobility and Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS): Shared mobility services offered by car-sharing platforms enable fleet optimization and help reduce the number of vehicles on the road, leading to more efficient use of resources.
End-of-Life Vehicle Management Systems: Technologies that facilitate the tracking and managing of vehicles at the end of their life cycle, ensuring proper disposal and recycling.
Recent Global Developments in this space
- November 2022: Renault has announced plans to split its business into five units, aiming to achieve closed-loop circularity across the vehicle life cycle. The last unit, “The Future is NEUTRAL,” aims to become carbon-negative in automotive production by 2030.
- October 2022: Stellantis plans to launch a circular economy business unit to become carbon neutral by 2038, generating €2bn in revenue.
- March 2021: Ford has set an interim target of using 20% recycled and renewable plastics in new vehicle designs by 2025. The current directive requires a minimum of 85% reuse and recycling and 95% reuse and recoverability for light vehicles.
- General Motors has stated that it will use 100% renewable energy for vehicles manufactured in the US and reduce factory greenhouse gas emissions by 31%, even as a raft of automakers, including Honda, Nissan, Toyota, and Volvo, are working to achieve carbon neutrality by 2031-2050.
- Japan and South Korea have had similar vehicle recycling laws for more than 15 years now. Meanwhile, India also launched a similar framework for scrapping end-of-life vehicles (ELVs) in August 2021. In the US, there is no federal law for ELVs, but several state governments have legislation and requirements for vehicle recycling.
Sources: Wiley, Economist Intelligence EIU.
Ostara Updates!

We are thrilled that our in-house insights for fund-raising in the Indian EV ecosystem for the period Jan – Aug 2023 were recently published in the Economic Times. Click here to read the article.

Our Founder, Vasudha Madhavan, appeared on the Energizing India Podcast, India’s only eMobility-focused podcast, for a record third time! In this engaging conversation, she shared her insights on Finding Investors for EV startups through the funding winter and other remarkable trends in the Indian EV ecosystem. Click here to listen to the podcast.
Do write to us with topics in Climate-tech, Mobility, and New Energy that you’d like us to cover in future editions.
















